
IN OTHER LANGUAGES
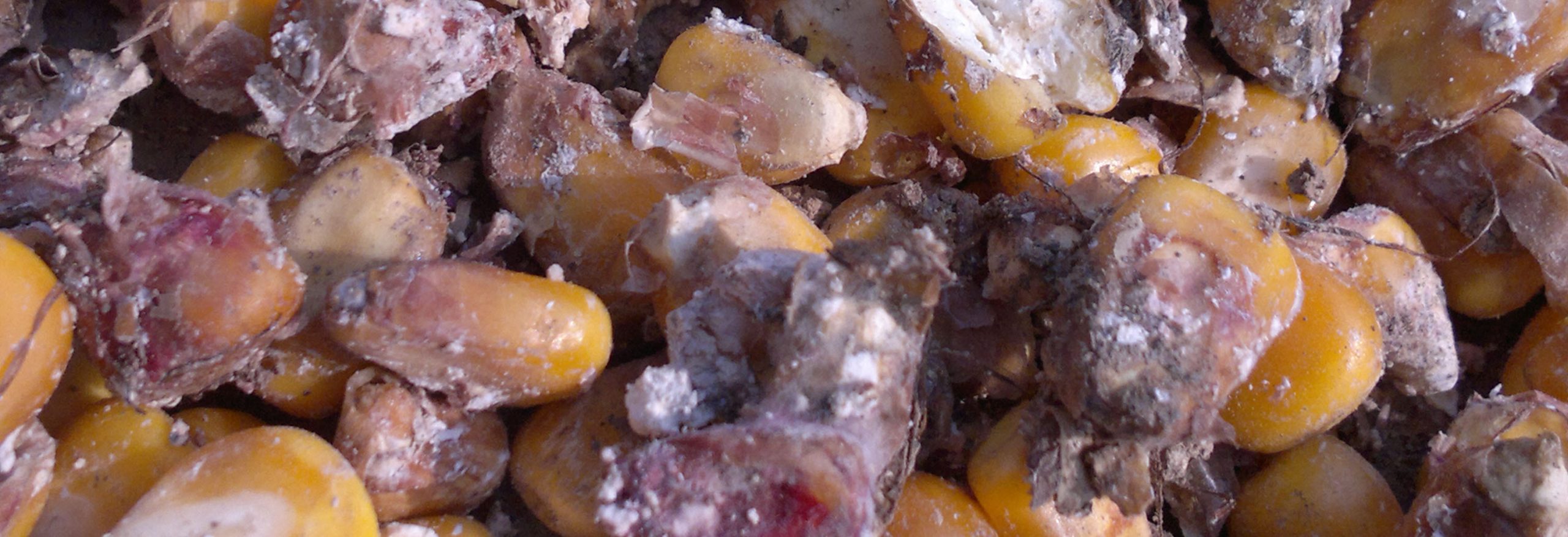

Mycotoxins are secondary metabolites produced by fungi when they grow on agricultural products before or after harvest, during transportation, or storage. The molds most commonly involved belong to the genera Aspergillus, Penicillium, and Fusarium.
Mycotoxins pose a severe threat to humans and as well as causing huge economic losses in the feed and food industries. These toxic substances are known to be either carcinogenic (e.g. aflatoxin B1, ochratoxin A, fumonisin B1), oestrogenic (zearalenone), neurotoxic (fumonisin B1), nephrotoxic (ochratoxin), toxic to the epidermis (trichothecenes) or immunosuppressive (aflatoxin B1, ochratoxin A and T-2 toxin).
The best-known consequences of mycotoxins are their clinical (diseases) and subclinical (productivity losses) effects on farm animals. The reduction of the value of raw materials and complete feeds is a lesser-known but very important repercussion.

Broilers are less sensitive to mycotoxins due to their short life cycle. Digestive lesions and failure of antibiotic-free programs are the most common consequences of mycotoxins.

In layers and breeders, mycotoxins reduce productivity by 0.08 eggs/hen/week, on average, and increase the occurrence of eggs with defects (thin-shelled and cracked eggs, pale yolks, etc)

Ducks, geese, and turkeys are more sensitive to mycotoxins than chickens. The most common signs are low body weight, increased mortality and oral lesions.

In rabbits, mycotoxins disrupt the reproductive cycle, reduce feed intake, make the animals prone to digestive infections and increase mortality.

Pigs are extremely sensitive to mycotoxins. Digestive, respiratory, and immune alterations, disruptions of the reproductive cycle, productivity losses, and failure of AGP-free programs are the most common consequences of mycotoxicosis.

Ruminants are less sensitive to mycotoxins because microorganisms present in the rumen are able to totally or partially detoxify certain toxins.
The risk by mycotoxin contamination is often overlooked by the aquaculture industry, but shrimps and fish are quite sensitive to mycotoxins and the occurrence of contaminated feeds is high.

The reduction of the value and utilization of feedstuffs is a lesser-known but very important repercussion, key for the economic success of the farm.
BioShield©, is a complete solution that protects your animals against toxicity by mycotoxins. It includes:
PlusBind© is a mixture of carefully selected silicates intended for the prevention of diseases and productivity losses related to the presence of all types of mycotoxins. It is indicated in poultry, pigs, aquaculture and ruminants.
The silicates present in PlusBind© have a highly expandable molecular structure. This characteristic gives the product a wide surface available for the adsorption of mycotoxins and therefore allows high effectiveness at low doses.
PlusBind Bio© is a premium mycotoxin binder intended for poultry, swine, and aquaculture.
It contains two types of ingredients:


Certain health statements may not be applicable in your region.